Microglia Transmit Pain to the Brain During Stress
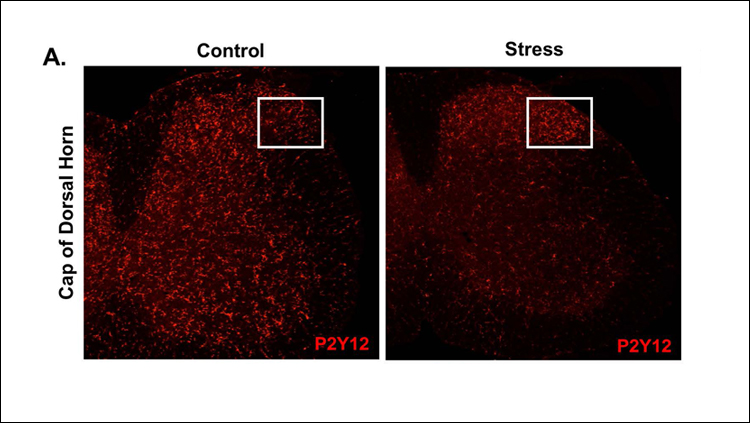
Research in male mice published in JNeurosci demonstrates activation of microglia in the spinal cord is responsible for increased pain sensitivity in response to stress.
John Sheridan and colleagues identified an inflammatory environment in the spinal cord caused by repeated exposure to an aggressive mouse — an established model of psychosocial stress — that accompanied lower pain thresholds observed in the stressed mice. Stress increased expression of inflammatory genes and activation of microglia in spinal cord regions involved in pain processing. Eliminating microglia from the spinal cord prevented these effects. These findings suggest a new cellular target for alleviating stress-induced pain.
Article: Microglia Promote Increased Pain Behavior through Enhanced Inflammation in the Spinal Cord During Repeated Social Defeat Stress
Corresponding author: Johnathan Godbout (The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, USA), Jonathan.Godbout@osumc.edu





















